The Gambling in Canada

Compared to other countries with legalized gambling, Canada cannot be called a gambling capital. Still, gambling is being developed pretty successfully there.
As of 2016, Canada has these numbers in gambling:
- 114 casinos
- 12 tracks for horse racing
- 1 bookmaker office
- 8 bingo halls.
The biggest part of casinos is in Alberta and Ontario provinces – they have 31 and 32 institutions respectively. The least number is in Yukon and Islands of Newfoundland and Labrador, and Prince Edward Island – 1 casino in each.
The gambling laws in Canada
The gambling in Canada is controlled by Articles 204, 206, 207 of the Criminal Code. These are basic Articles used to create the other legal documents with a bigger number of specificities on the regional level.
- Article 204 defines the rules of horse race and their sweepstakes
- Article 206 defines the list of prohibited gambling activities and actions
- Article 207 defines the list of allowed gambling activities and actions.
Thanks to this law, every province is free to create own lotteries and deal with gambling.
The regulation of gambling depends on provinces. The country has 13 states and each of them has own rules in gambling and its legislation.
History of gambling in Canada
When the pioneers of Canada came on the local lands in the 15th century, they discovered that local tribes were playing a lot of gambling. These carried the great sense for the spiritual and mystical matters. That is why gambling is not new to Canada.
English pioneers have brought the ages-long prohibition on gambling. The English King Richard the Third prohibited gambling in 1380 considering that his warriors had too much time spent on gambling.
In 1892, the Canadian Criminal Code once again reinforced the prohibition. Since then, laws were gradually softened. Bingo and raffle were allowed for charity purposes in 1900. In 1969, the government understood that gambling might be a beneficial business for the state.
The first lottery of this kind was organized in 1974 to finance the Olympics in Montreal.
The legalization of gambling in Canada
The society changes in 1970's triggered the multi-billion growth of the gambling business in Canada. In 1989, the first commercial casino opened in Winnipeg. The second one opened in 1993 in Montreal.

Then, on March 15, 1999, the Canadian government in Ottawa completely legalized gambling and allowed its regional official bodies earning on it, opening online or offline lotteries and casinos.
The first among others in adopting the legislation in gambling were Quebec, Manitoba, and Nova Scotia.
- In Quebec, the proper acts were adopted in 1978. These are two acts: Act respecting the Societe des loteries du Quebec and Act respecting lotteries, publicity contests, and amusement machines
- Manitoba adopted Manitoba Lotteries Corporation Act in 1993 and Gaming Control Act in 1996
- Nova Scotia adopted the Gaming Control Act in 1995.
Gambling in modern Canada
As of 2016, gambling in Canada is being developed fairly productively. As it has already been stated, 114 casinos, 12 tracks for horse racing, 1 bookmaker office, and 8 bingo halls successfully operate in the country.
The Canadian casinos have 1,776 tables for card gambling, 220 poker tables, and 57,150 slot machines. Many casinos in Canada are nothing inferior to the American ones in Las Vegas and Atlantic City.
The biggest part of them works in Ontario province. It has 32 institutions, 666 card tables, 26,022 slot machines, and video pokers.
The most known casinos in Canada
The most known and biggest casinos in Canada are Casino Niagara and the Niagara Fallsview Casino Resort. They are located close to the famous Niagara Falls in Ontario. The casino offers their guests thousands of slot machines and hundreds of tables with card gambling.
The most famous horse race track and rasino are Woodstock Racetrack and Slots. It is also located in Ontario. More than a hundred slots are in its hall.
Except for Ontario, there are provinces that intensively develop their gambling business. These are Alberta and Nova Scotia. Alberta has a city with the highest concentration of casinos; Edmonton has 9 casinos with 200 card tables, 5,400 slots, and video pokers.
Taxation of wins in Canada
Canada does not make taxation of wins if only they aren’t stated in the form of earning. The earning from winning, according to the Canadian legislation, differs in these three things:
- Existence of the specific skills
- The regularity of payouts
- Expectancy of the next payouts.
That is, taxes may be collected from the professional gamblers but should not be collected from those who play for fun.
The most widespread gambling in Canada
The most widespread gambling in Canada is slot machines and electronic gambling machines (EGM). The most part of them is in Ontario – 22,198 pieces.
The other gambling includes:
- lottery tickets machines – only in Ontario
- electronic bingos
- electronic and offline card tables
- Internet gambling.
British Columbia has the biggest quantity of electronic bingo machines – 4,069.
The biggest number of electronic and offline card tables is in Ontario – 1,101.
Internet gambling must be separately mentioned. Not every province allows it. For instance, Internet gambling is inaccessible in Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Ontario. The other provinces consider it legal.
Internet gambling in Canada embraces:
- instant scratch cards
- lotteries
- bingo
- casino slots
- board games
- Ingenio
- poker
- sports betting
- video poker.
Every province has its own set of allowed Internet gambling. For instance, only the Ingenio is prohibited in British Columbia. On Prince Edward Island and in Nova Scotia, only scratch cards, lotteries, and bingos are allowed.
Alberta Province holds the largest number of charitable gambling licenses – 15,055. It should be noted that in the number of such licenses usually included only those organizations, which sales revenue is more than USD 10,000. The exceptions are Nova Scotia, Ontario, and Manitoba.
Online gambling in Canada
Online gambling in Canada today is regulated by the same Articles of the Criminal Code. It doesn’t say now that online gambling is prohibited. The responsibility is borne by the organizers of gambling – if a gambler is a minor or the actions fall under the mentioned Articles.
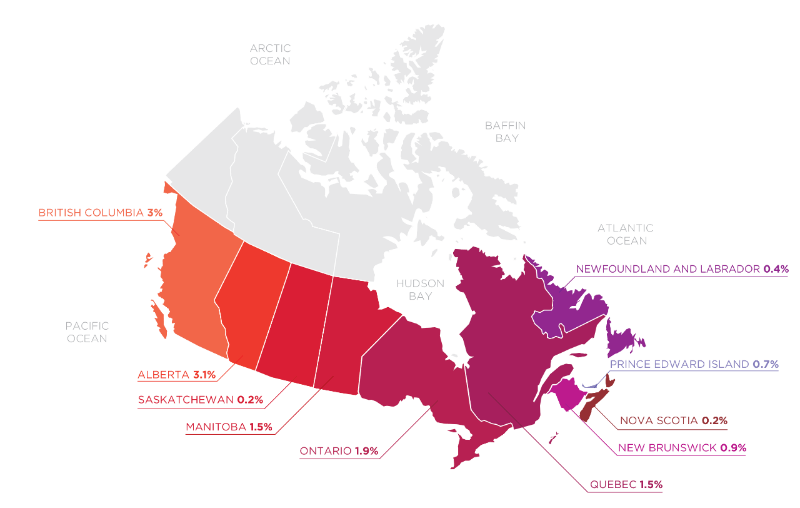
Thus, despite the fact that online gambling is allowed in Canada, in the most cases and provinces, one can gamble only in the governmental lottery. However, there were no cases yet when a person was charged with a fine or imprisonment for online gambling.
The history of online gambling in Canada
Before 2009, Internet sites with gambling were prohibited in Canada. However, Canadians played offshore Internet sites with gambling and the legislation did not have a penalty for that.
The strictest prohibition for online gambling in Canadian history was in 2007 – when Kahnawake Mohawk reservation was fined for 2 million dollars and its servers of online casinos and poker rooms were acknowledged illegal. After the fine was paid, the reservation continued to be engaged in this business and all its servers were restored and work until now successfully.
Slot machines in Canada
The ambivalent situation with gambling online does not prevent Canadians from playing in the online casinos. Below, we represent you the list of online casinos with the gambling machines that are very popular amongst the Canadians:
The gambling business in Canada is an example of successful cooperation between authorities and organizers of the casinos. Thanks to gambling institutions, provinces receive a good income in their budgets. Gamblers can play without worries and without fear of prohibitions. Consequently, Canada is characterized by a very low percentage of people sick with gambling dependence.





